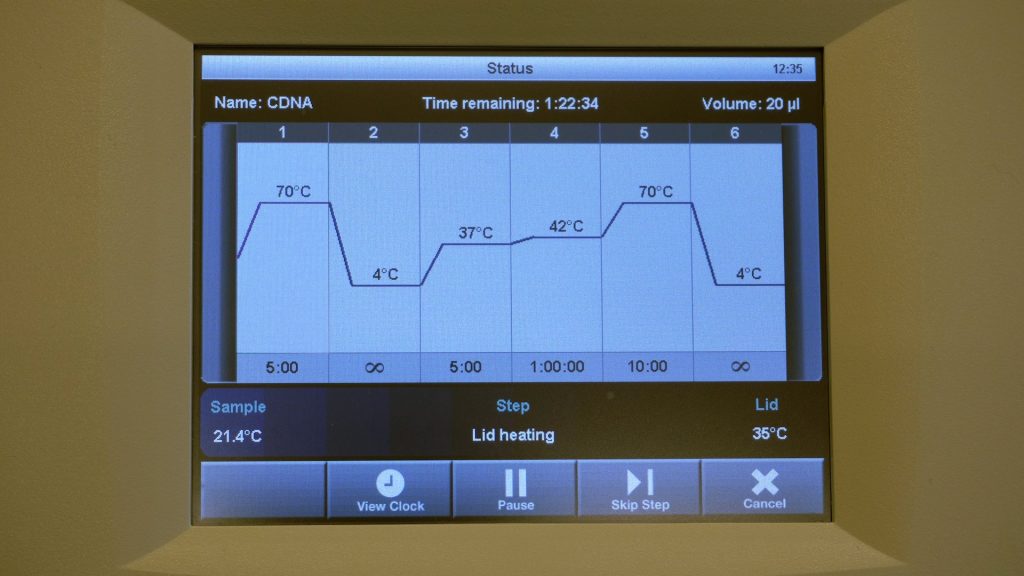
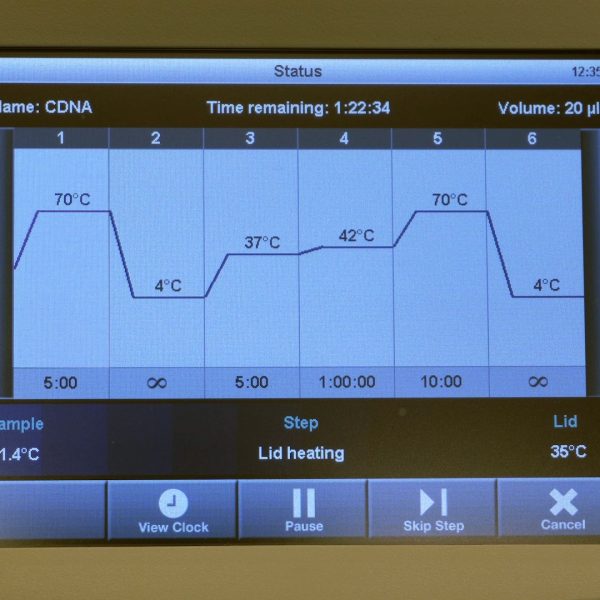
cDNA synthesis
This video shows how to synthesize cDNA from isolated RNA.
- Tineke Bijl
-
(0)
- 0 enrolled students
Description
Non-interactive video download link (mp4).
The script that has been used to create the video shown above can be downloaded as excel script file.
| 1 | For the cDNA synthesis you need 0.5 µg RNA per sample. Using your obtained RNA concentration calculate the amount of µL that you need from your sample in order to obtain 0.5 µg RNA. Have the calculation checked by the assistant! | |
| 2 |
| |
| 3 | Pipette a noRT-controle in the tube marked as noRT-controle:
NB: Where is this controle for? If you have read the protocol neatly in prepare mode, you will know this. | |
| 4 |
| |
| 5 | Remove the samples from the PCR machine and immediately put them on ice. | |
| 6 | For the no RT-controle, add to your control tube:
| |
| 7 | Make a “master mix” stock solution for the other samples.
| |
| 8 |
| |
| 9 | Put the 9 samples back into the PCR device and continue the RT program:
| |
| 10 | For samples where 0,5 µg RNA was used in the first step: add 180 µL Milli Q. | |
| 11 | For samples with less than 0.5 µg of RNA added in the first step: Calculate the amount of Milli Q to be added so that the final concentration of cDNA matches the other samples. Consider the reaction volume of the RT-PCR reaction and have your calculation checked by the assistants before adding the Milli Q. | |
| 12 | Transfer the diluted sample to a 1,5 ml eppendorf tube, clearly labeled with:
| |
| 13 | Store the cDNA samples in the -20° C freezer overnight. | |
The following calculation is aimed at samples up to 100 ng/µL. Which of the following calculations is/are correct (more answers are possible)? Assume the concentration of your sample is 1300 ng/µL and that the available volume in which the RNA is dissolved in Milli-Q is 20 µL (=desired/available total volume). What volume of RNase-free Milli-Q needs to be added?
Feedback if correct: Correct! There are two ways in which this calculation can be done correctly. Using the C1 * V1 = C2 * V2 (C = concentration, V = volume, 1 and 2 referring to the concentrations and volumes that we have and we want with one unknown value), and by using a dilution factor in the calculation, where we divide the two concentrations and use 1/dilution factor * end volume formula Feedback if a: Incorrect! The unknown value in this question is V2. The known concentration of your sample is 1300 ng/µL, the concentration you want is 100 ng/µL. We also know that the available volume in which the RNA is dissolved in Milli-Q is 20 µL (V1) Feedback if b: Incorrect. In this calculation V2 = 260 µL. However, this is the end volume and not the volume we need to add. V2 should be the amount of RNA-free Milli-Q we need to add, which is calculated by the end volume – available volume in which the RNA is dissolved in Milli-Q. Feedback if d: Incorrect. In this calculation the wrong concentration is used for the dilution step. |
For cDNA synthesis we have diluted the samples to a RNA concentration of 100 ng/µL (see previous question). It is however possible that your sample already had a lower concentration than 100 ng/µL. The next step is to calculate the volume of sample needed in order to have an amount of 0.5 µg RNA to insert into the qPCR machine. This amount is referred to as the VRNA. Which of the following calculations is/are correct (more answers are possible)? Keep in mind that a maximum of 12.75 µL RNA can be used for the cDNA synthesis.
Feedback if correct: Correct! By calculating and then diluting all of the samples to 100 ng/µL in the previous question we standardized all samples. For each sample with this concentration we will need to add a set amount of µL = VRNA in the PCR Eppendorf for the subsequent experimental steps. This means that this calculation depends on your previous lab work. As the total RNA needed for the qPCR experiment is 0.5 µg, the set amount is 50 µL by dividing the µg by µL to keep the right entity. However, sometimes the original RNA concentration is already below 100 ng/µL and then this set amount does not apply Feedback if c: Incorrect. The total amount exceeds the maximum amount that can be used for cDNA synthesis Feedback if b: Incorrect. There is a mistake in this calculation regarding a decimal point. |
Waarom is het nuttig om een no-RT controle sample mee te nemen?
o Incorrect. Wat bevat een no-RT controle sample? Kun je daarmee controleren of het proces goed verlopen is? |
Waarop is de keuze voor Oligo dT als primer gebaseerd? Er kunnen meerdere antwoorden goed zijn.
Feedback if correct: Juist! Oligo dT bindt aan de polyA staart van mRNA waardoor cDNA synthese plaats kan vinden, gekatalyseerd door het enzym reverse transcriptase. Feedback if incorrect: Wil je hier de genen van interesse al selecteren? |
Download zip to import in LabBuddy.
Please make sure that your product exists and valid for this course
- Skill levelIntroduction video
- CategoryMolecular biology
Related videos
-
Free
qPCR
-
Free
cDNA synthesis
-
Free
RNA isolation
Copyright information
This video is created by Leiden Academic Centre for Drug Research (LACDR), Faculty of Science at Leiden University under a open Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License. When using this video in its original version please refer to www.labprep.video. When adapting the video, mention the source ‘adapted based on the original version that is created by the labprep.video team’. It is not allowed to use the video for commercial purposes without consultation with the creators. You can contact us via info@labprep.video.